You Have the Clean Power to Go Electric
Going electric refers to the transition from relying on fossil fuels as an energy source to using clean electricity to power various aspects of our lives, including cars and home appliances.
Going electric makes homes safer and more efficient, especially as more renewable energy is added to the grid. In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards going electric, as individuals seek to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and transition to clean energy. This is where Silicon Valley Clean Energy (SVCE) comes in. We are the local electricity provider for 13 communities in Silicon Valley and provide clean energy to our customers so that they can go electric with confidence.
Using clean electricity to power our vehicles and homes is one of the ways we can take climate action. The SVCE eHub has free resources designed to help take the guesswork out of going electric including information on electric appliances, electric vehicles, and home solar and battery systems.
Go Electric When You Drive
Going electric when you drive is one of the most impactful actions you can take to reduce emissions in our community. Gas vehicles are the largest source of harmful greenhouse gas emissions in Silicon Valley. Upgrading to an electric vehicle (EV) significantly lowers emissions since they do not burn gasoline and SVCE customers can charge their car with our clean power mix.

According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), a typical passenger vehicle emits about 4.6 metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) per year. A gallon gasoline burned emits about 20 pounds of CO2. Alternatively, an electric vehicle (EV) has zero tailpipe emissions and does not use gas! A common question we receive is about the emissions associated with charging an EV, and for this you just have to look at the emissions on the grid, which is calculated from how energy is generated. So, driving an EV charged from the California grid “emits” only 0.98 metric tons of CO2 per year. This number is even less for SVCE customers who receive cleaner power than the state average.1
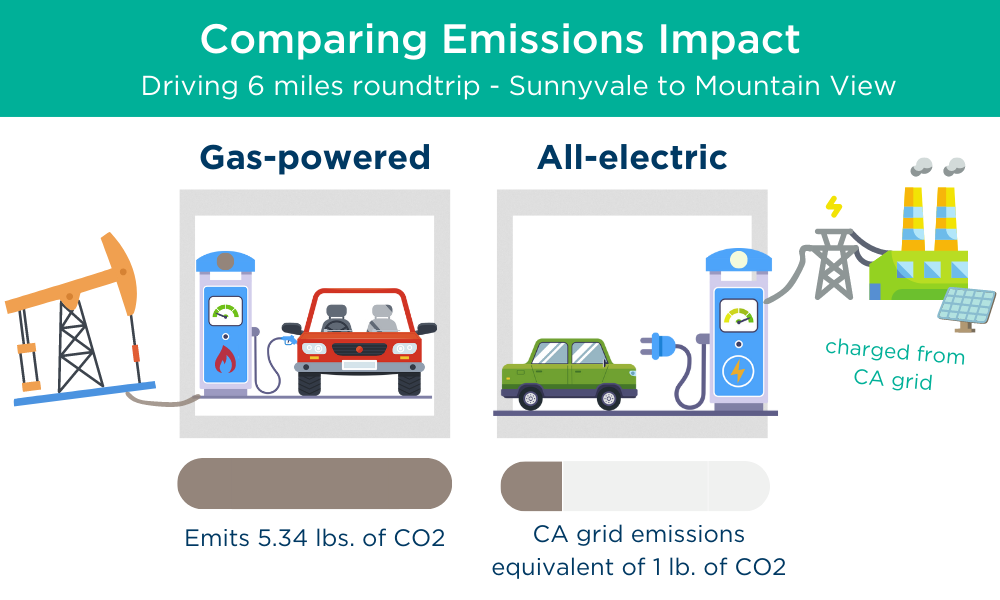
EVs have no tailpipe emissions; however, emissions are created generating the electricity used to charge the car. Visit the Beyond Tailpipe Emissions calculator to view how emissions change regionally.
Based on August 2022 DMV data, approximately 40,400 SVCE customers are already driving electric. There are various rebates, including federal tax credits and state incentives, to help reduce the cost of buying or leasing an EV. EVs also offer a great driving experience. EVs have instant torque, providing a smooth and quiet driving experience plus improved acceleration. Explore your EV options and incentives at svcleanenergy.org/drive-electric.info
1 This assumes the typical passenger vehicle drives 22.0 miles per gallon and drives around 11,500 miles per year. Every gallon of gasoline burned creates about 19.6 lbs. of CO2 and the typical passenger vehicle emits about 0.89 lb. of CO2 per mile. To put it in perspective, this means that a typical passenger vehicle emits 5.34 lbs. of CO2 for every 6 miles driven.
Comparing emissions, this assumes the typical EV drives 2.9 miles per kWh and drives around 11,500 miles per year. Based on California’s 2022 average electricity mix, 0.456 lb. of CO2 per kWh is emitted and the typical EV emits about 0.17 lb. of CO2 per mile. To put it in perspective, this means that a typical EV emits 1 lb. of CO2 for every 6 miles driven. This number is less than a pound for SVCE customers.
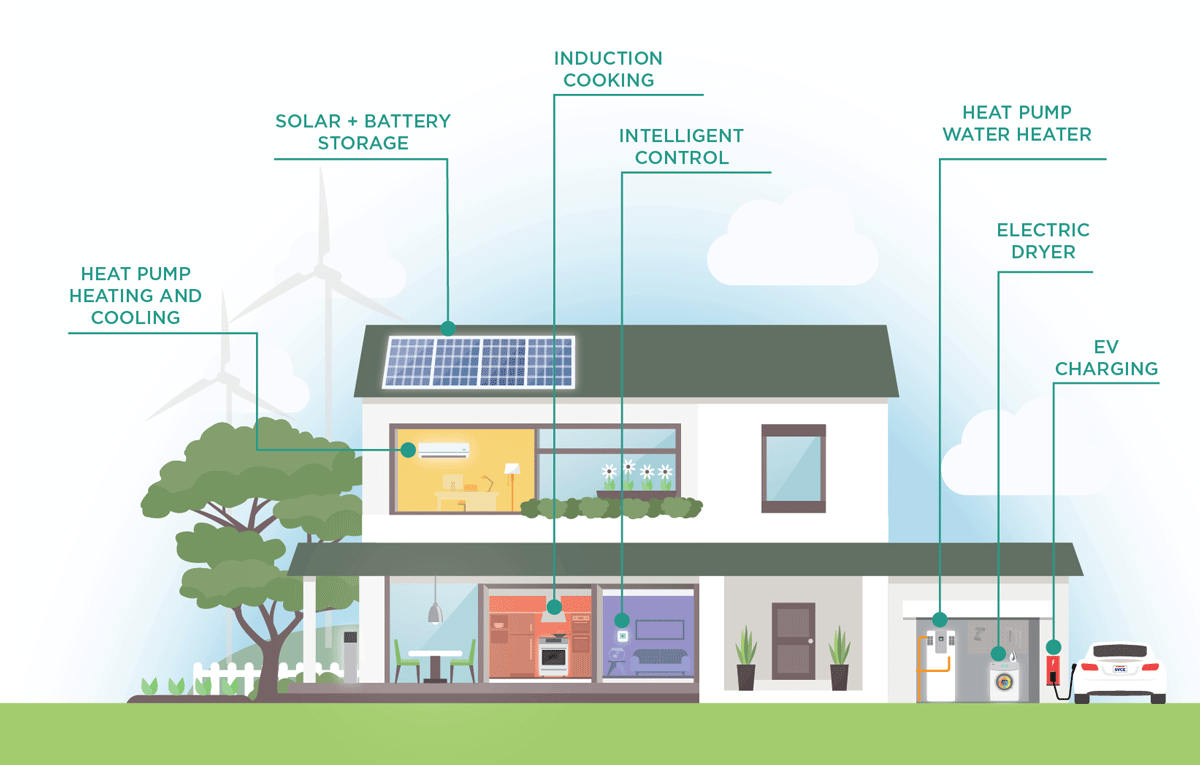
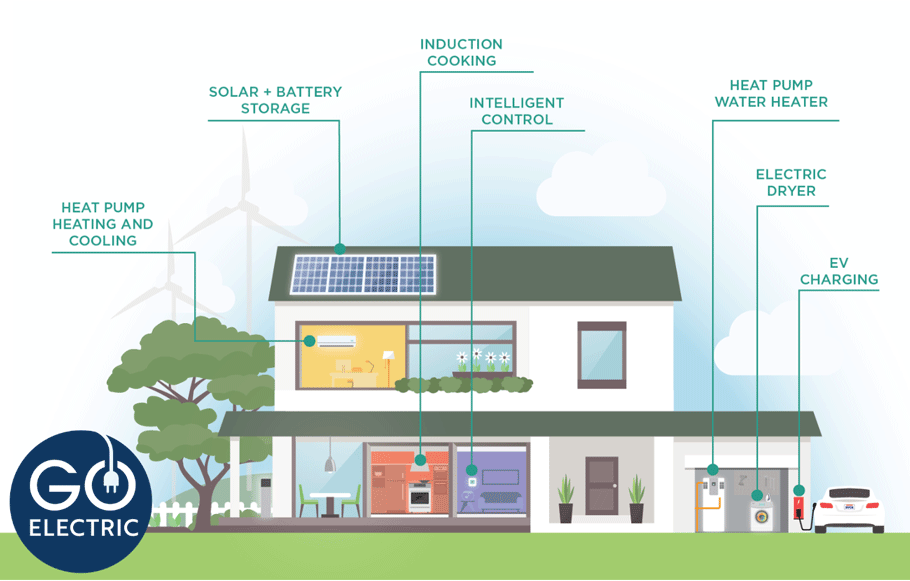
Go Electric in Your Home
By going electric in your home, you can enjoy numerous benefits, including saving energy with more efficient appliances, improved indoor air quality, and increased comfort, all while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. As an SVCE customer, you can receive rebates to remove old gas appliances from your home and upgrade to clean, electric appliances.
Gas water heaters and heating systems are typically a home’s biggest source of emissions, and they contribute to poor air quality in our community. According to SVCE’s emissions inventory, emissions from buildings account for nearly 50% of regional pollution.
Heat pump water heaters, are more efficient than their gas counterparts since they move heat from the surrounding air and transfer it to the water in an enclosed tank without combustion. Heat pump space heating and cooling systems work by taking heat from surrounding areas and moving it to another location. Heat pump systems use energy-efficient technology to not only keep your home cool when it’s hot outside, but also heat your home when it’s cold, resulting in ideal temperatures year-round.

Cooking with a gas stove releases carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, and other pollutants into your home – emissions that are toxic for you and your family. A clean alternative is using induction cooktops. Induction cooktops use clean electricity to transfer currents from the electromagnetic field beneath the cooktop to the cookware. Induction technology releases no toxic pollutants, is safer, and heats faster. To learn how you can upgrade your cooking experience and improve the air quality in your home, check out our dedicated blog post about induction cooking here.
Explore more ways you can go electric in your home by visiting svcleanenergy.org/electric-home.
Start Your Journey to Go Electric
Going electric when you drive and, in your home, can bring countless benefits, including improved performance and comfort, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. At SVCE, we are dedicated to providing our customers with clean energy and offering the support you need to go electric with confidence. Start your journey to Go Electric by visiting svcleanenergy.org/ehub.